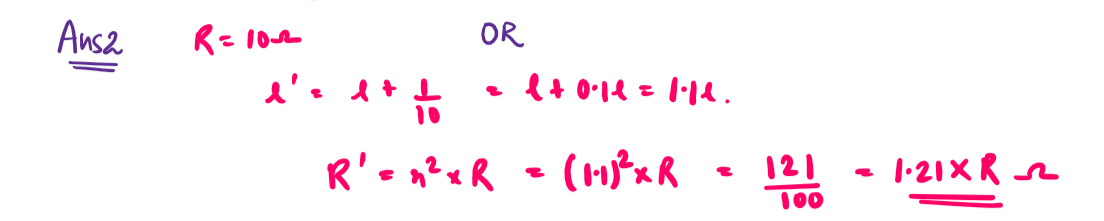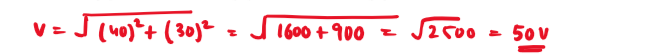1. In which of the following substances, resistance decreases with the increase of temperature ?
Explain:- For carbon, resistance decreases with increase in temperature.Some materials that have decreasing resistance with increasing temperature include: Carbon, Copper, Mercury, Platinum
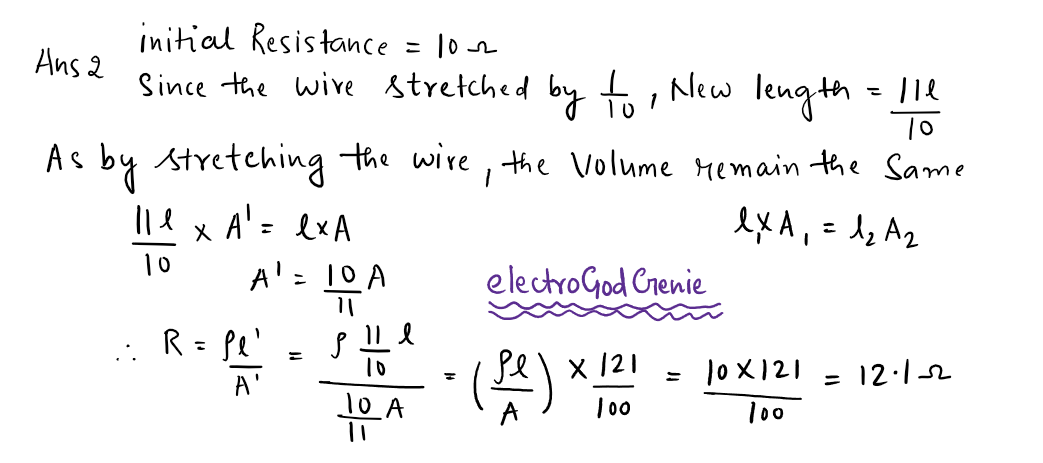
2. A wire has resistance of 10 ohm It is stretched by one-tenth of its original length, then its resistance will be
Explain:-
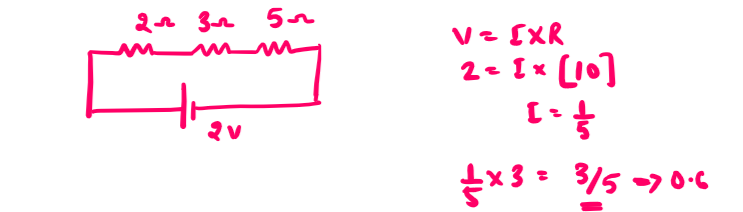
3. A cell of negligible resistance and emf 2 volts is connected to series combination of 2, 3 and 5 ohms. The potential difference in volts between the terminals of 3 ohm resistance will be
Explain:-
4. Two electric bulbs rated p1 watt , V volt and P2 watt V volt are connected in series across V volt. The total power consumed is
Explain:-
5. A primary cell has an emf of 1.5V. When short circuited, it gives a current of 3A. The internal resistance of the cell is
Explain:- r = E / I = 1.5 / 3 = 0.5 ohm
Internal resistance formula
Ohms are used to measure internal resistance. The connection between internal resistance (r) and electromotive force (e) in cells is given by.
I (r + R) = e
Where e is the electromotive force (Volts), I is the current (A), R is the load resistance, and r is the cell’s internal resistance in ohms.
e = V + I r or e = IR + I r
V is the potential difference (terminal) across the cell while the current (I) is flowing through the circuit in the equation above. The following is the connection between Internal Resistance represented by r and emf denoted by e of a cell:
I (r + R) = e
Where we can see that the quantity symbolized by the letter e = EMF, also known as the electromotive force of Volts, is expressed as:
I = current, denoted by A, R = Load resistance, and r is the Internal resistance of a cell measured in ohms.
Rearranging the equation above yields the following:
In other words, e = IR + Ir or e = V + Ir.
Note that a cell’s emf (e) is always bigger than the cell’s potential difference (terminal).
6. Two identical heaters each marked 100 W, 250 V are placed in series and connected to 250 V supply. Their combined rate of heating is
Explain:-
9. The relative permeability of a material is 0.9998 . It is
Explain:- ( i ) If relative permeability of medium is 0.999 ( slightly less than 1 ) , it is diamagnetic substance .
( i i ) If relative permeability of medium is 1.001 ( slightly greater than 1 ) , it is a paramagnetic substance .
11. The SI unit of reluctance is
Explain:- Magnetomotive Force -- The quantity of magnetic field force, or "push." Analogous to electric voltage (electromotive force).
Field Flux -- The quantity of total field effect, or "substance" of the field. Analogous to electric current.
Field Intensity -- The amount of field force (mmf) distributed over the length of the electromagnet. Sometimes referred to as Magnetizing Force.
Flux Density -- The amount of magnetic field flux concentrated in a given area.
Reluctance -- The opposition to magnetic field flux through a given volume of space or material. Analogous to electrical resistance.
Permeability -- The specific measure of a material's acceptance of magnetic flux, analogous to the specific resistance of a conductive material (ρ), except inverse (greater permeability means easier passage of magnetic flux, whereas greater specific resistance means more difficult passage of electric current).
12. A 2 cm long coil has 10 turns and carries a current of 750mA. Two magnetising force of the coil is
Explain:-
13. If the number of turns of a coil is increased, its reluctance
Explain:- A greater number of coil turns will result in a higher inductance, all other things being equal. When the coil's turns are reduced, the inductance also decreases. Inductance increases with increasing wire turns in the coil and decreases with decreasing wire turns in the coil, all other things being equal.
14. The internal resistance of lead acid battery is mainly due to
Explain:- The opposition offered to current within the cell is called the internal resistance of the cell. It is made up of the resistances of the plates, the active material and the electrolyte, but it is mainly due to electrolyte.
The internal resistance of lead acid cell is very small(0.1 ohm) and depends upon the following factors.
1. Area of plates:decrease with increase in plate area.
2. Spacing between plates:decrease with the decrease in spacing.
3.Specific gravity of electrolyte:decrease with increase in specific gravity.
15. A 100V peak AC is as effective as ______ dc
Explain:- V peak = 100 V. since, we already know that dc voltage is equal to the ac peak voltage divided by √2. Vdc = 70.7 V. therefore, the dc voltage of the 100V peak ac voltage is 70.7 V.
16. The form factor of a sinusoidal wave is
Explain:- The form factor of a sinusoidal wave is 1.11. The form factor is defined as the ratio of the root mean square (RMS) value to the average value of the wave. The formula for form factor is:
1.Form factor = mathematical mean of absolute values of all points on the waveform / Root mean square value
2.Form factor = Vrms/Vav = (Vp/√2)/0.637Vp
The average value of a sinusoidal wave is 0.637 times the peak value. The average value of a sinusoidal wave over one complete cycle is zero because two halves cancel each other. The average value is taken over half a cycle.
17. In a series L-C-R circuit the voltage across R, L and C are 40V, 50V and 20V respectively. The voltage of applied source is
Explain:-
19.The impedance of a circuit is 10 OHM. If the inductive susceptance is 1 S, then inductive resistance of each phase is
Explain:-
21. A 3 phase load is balanced if all the three phases have to same
Explain:- A balanced three-phase voltage or current is one in which the size of each phase is the same, and the phase angles of the three phases differ from each other by 120 degrees. A balanced three-phase network is one in which the impedances,pf,resistance in the three phases are identical.
23. Permanent magnet moving coil instrument can be used for
25. A moving coil instrument having meter resistance of 5 ohm is to be used as a voltmeter of range 0-100 V. If the full scale deflecion current is 10 mA, then required series resistance is
Explain:-
26. An oven takes 16A at 220 V. It is desired to reduce the current to 12A. The value of resistance will be
Explain:-
33.A three-phase load is said to be a balanced load, if all the three phases have same
35.The emf induced in the secondary winding of a 50 Hz single-phase transformer having 1000 turns on its secondary is 222 V. The maximum flux density in the core is 0.1Wb/m2. The cross-sectional area of the core is
Explain:-
36.A transformer when supplying a load maintained 11 KV across load terminals. When the load was switched off, the terminal voltage became 11550V.What is the voltage regulation at this load ?
Explain:-
38. The phenomenon of squirrel cage motors sometimes showing a tendency to run at a very low speed is known as
Explain:-
43. In a single phase repulsion motor, torque is developed on the rotor when Brush axis is fixed
Explain:-
46.In direct heating method, maximum heat transfer takes place by
Explain:- Resistance Heating:
When current passes through a resistance, power loss takes place, which appears in the form of heat.
Power loss = I2R = V I = V2 / R watt Where, I is the current V is the voltage R is the resistance
(A) All the electrical energy given to a resistance heating element will be converted into heat energy.
(B) The loss of energy takes place only in transferring heat from element to charge or load.
(C)The resistance heating is further classified as
(1) Direct Resistance Heating
(2) Indirect resistance heating
(3) Infrared or Radiant heating
In the direct resistance heating method, the maximum heat transfer takes place by conduction. or In InDirect Resistance method,the maximum heat transfer take place by Radiation.
51.Photovoltaic cell is an/a _________ transducer.
Explain:- Photovoltaic Cell as an Optical Transducer
A photovoltaic cell acts as an optical transducer by converting light energy (optical energy) into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect.
How It Works:
1.Incident light (usually sunlight) strikes the semiconductor material (like silicon).
2.Photons in the light excite electrons, creating electron-hole pairs.
3.These charge carriers are separated by the internal electric field of the p-n junction.
4.A voltage is generated, producing a direct current (DC) output when connected to a load.
52.Electrostatic voltmeters are used to measure voltage across
Explain:- Electrostatic voltmeters are ideal for measuring the voltage across capacitors because they:
1.Measure voltage without drawing current
2.Prevent capacitor discharge during measurement
3.Accurately measure high voltages in high-impedance systems
53. The speed error of the energy meter is corrected by adjusting the position of______ magnet.
Explain:-
54.A Synchroscope is used to _______ an alternator with bus bar.
Explain:- A synchroscope is used to synchronize an alternator with a bus bar through phase displacement, by indicating the difference in phase angle and frequency between the incoming alternator and the bus bar.
Explanation:
1.Phase displacement refers to the angular difference between the voltage waveform of the alternator and that of the bus bar.
The synchroscope shows this displacement by the rotation of its pointer:
1.If the pointer rotates, the alternator is out of phase.
2.If the pointer is stationary at the 12 o’clock position, the phase, frequency, and voltage match — and the alternator can be safely synchronized with the bus
55.Heat sinks are used in power amplifier circuits
Explain:- Heat sinks are used in power amplifier circuits to increase the collector dissipation rating of the transistor. This is because power amplifiers operate at high power levels and generate a lot of heat, which can damage the transistor if it is not dissipated properly.
A heat sink is a passive component that is used to transfer the heat generated by the transistor to the surrounding environment, thus reducing the temperature of the transistor and increasing its reliability.
Benefits of using heat sinks:
1. Increases the Collector Dissipation Rating: A heat sink increases the collector dissipation rating of the transistor by providing an additional surface area for heat dissipation. This helps to prevent the transistor from overheating and getting damaged.
2. Reduces the Thermal Resistance: A heat sink reduces the thermal resistance between the transistor and the surrounding environment, which allows heat to flow away from the transistor more easily.
3. Increases the Reliability: By reducing the temperature of the transistor, a heat sink increases the reliability of the amplifier circuit. This is because high temperatures can cause the transistor to degrade over time, reducing its performance and lifespan.
Conclusion:
In summary, heat sinks are an important component in power amplifier circuits as they help to increase the collector dissipation rating of the transistor, reduce thermal resistance, and increase the reliability of the amplifier circuit.
56. The most essential condition for parallel operation of two 1-phase transformers is that they should have the same
Explain:-
57. The principle of dynamically induced e.m.f. is utilised in
Explain:- The principle of dynamically induced emf is utilized in a generator. Generators are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. They work based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which was discovered by Michael Faraday in the early 19th century.
Principle of Electromagnetic Induction:
According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, when a conductor is moved through a magnetic field or when the magnetic field through a conductor changes, an electromotive force (emf) is induced in the conductor. This emf is known as the dynamically induced emf.
Working of a Generator:
A generator consists of a coil of wire, known as an armature, which is placed inside a magnetic field. When the armature is rotated, the magnetic field lines passing through it change, and this change in magnetic field induces an emf in the coil.
Process:
1. When the armature is rotated, the magnetic field lines cut across the coil, causing a change in magnetic flux.
2. According to Faraday's law, this change in magnetic flux induces an emf in the coil, which results in the generation of electrical energy.
3. The magnitude of the induced emf depends on factors such as the number of turns in the coil, the strength of the magnetic field, and the speed of rotation.
4. The induced emf causes a flow of electric current through the coil, which can be used to power electrical devices or charge batteries.
Types of Generators: There are two main types of generators:
AC generators and DC generators.
AC Generators: These generators produce alternating current (AC), where the direction of the current changes periodically. The induced emf in an AC generator follows a sinusoidal waveform.
DC Generators: These generators produce direct current (DC), where the current flows in only one direction. The induced emf in a DC generator is converted to DC using a commutator.
Applications:
Generators are widely used in various applications, such as power plants, wind turbines, hydroelectric plants, and portable generators. They play a crucial role in generating electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes.
In conclusion, the principle of dynamically induced emf is utilized in a generator, where mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy through the process of electromagnetic induction.
58. The rotor of a 4-pole ac generator is wound with 200 turns coil. If the flux per pole is 5 mwb and the rotor runs at a speed of 1500 rpm, the rms value of the induced voltage for this ac generator is nearly
Explain:-
59. A 10 pole, 25 Hz alternator is directly coupled to and is driven by 60 Hz synchronous motor. What is the number of poles for the synchronous motor ?
Explain:-
60. Which of the following motors is not a synchronous motor?
Explain:- An induction motor is also called as asynchronous motor, because the actual speed of the motor is not equal to the synchronous speed of the motor. The synchronous speed of the motor is always more than the actual speed of the motor. If the actual speed of the motor (N) is equal to the synchronous speed (Ns), then no torque will be produced and motoring function not possible. So that an induction motor is called asynchronous motor.
The synchronous speed is the speed of rotating magnetic field which is produced when the three phase supply is fed to the stator of the motor.
The rotor conductors of an induction motor is short circuited at the end rings. The magnetic filed acts on the rotor. When the magnetic field gets linked to the rotor conductor the voltage is induced in the rotor conductor. The underlying principle is electromagnetic induction, which is similar to transformer working principle.
However, if the rotating magnetic field and rotor rotates at the same synchronous speed, the EMF induced in the rotor is zero because the field will be constant with respect to rotor. The voltage will be induced in the rotor if rate of change of flux exist.
The motor rotation happens when there is slip between the rotor and the stator. The slip is the difference between the speed of rotational magnetic field and the actual speed of the rotor. The inability of the rotor to catch up the speed of the rotating magnetic field is called the slip of motor. Thus, an induction motor working is possible if slip exist between rotating magnetic field and the actual speed of the rotor. As the load is increased on the motor its slip gets increased.
That is why an induction motor is also called as asynchronous motor."
61.The rotor of a stepper motor has
Explain:- "The rotor of a stepper motor typically does not have any winding, commutator, or brushes.
Concept:
Winding: Stepper motors are typically constructed with a stationary stator that contains the windings, while the rotor is designed without any windings. The stator windings create a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor's permanent magnets or teeth to generate motion.
Commutator: Stepper motors do not use a commutator, which is a device used in some types of motors to switch the direction of current flow in the rotor windings. Instead, stepper motors rely on digital control signals to energize specific stator windings in a precise sequence, allowing for controlled and precise angular movement of the rotor.
Brushes: Stepper motors do not have brushes, which are commonly found in brushed DC motors or certain types of AC motors. Brushes are used to transfer current to the rotor windings in motors that require mechanical commutation. Since stepper motors do not have a commutator or rotor windings, brushes are not needed.
"Therefore, all of the options mentioned in the question are correct. The rotor of a stepper motor does not have winding, commutator, or brushes."
62.Which of the following starting methods cannot be used for starting a 3-phase squirrel cage induction motor ?
Explain:- "In squirrel cage induction motor, the rotor terminals are short-circuited. Hence we cannot add external resistance into the rotor circuit. So we cannot use is this method for starting.
Important Points:
The star-delta starter method of starting three-phase induction motors is very common and widely used among all the methods. In this method, the motor runs at delta connected stator windings. It is also used for small motors up to 5 kW rating.
The direct on line (DOL) starter method of an induction motor is simple and economical. In this method, the starter is connected directly to supply voltage. By this method, small motors up to 5 kW rating are started to avoid the supply voltage fluctuation.
The Autotransformer is used in both the type of the connections, i.e., either star connected or delta connected. The autotransformer is used to limit the starting current of the induction motor. This method is used for the high rating of squirrel cage induction motors. So, this method is most suitable for a 20 kW squirrel cage induction motor."
63. Linear induction motor is used in
Explain:- Application of Linear Induction Motor:
1.Automatic sliding doors in electric trains.
2.Traction
3.Mechanical handling equipment, such as propulsion of a train of tubs along a certain route.
4.Metallic conveyor belts.
5.Pumping of liquid metal, material handling in cranes, etc.
64. The value of capacitor for a capacitor start IM is determined by
Explain:- The capacitor start induction motor is identical to a split phase-induction motor except that:
(1) Starting winding and main winding have equal number of turns
(2) A capacitor is connected in series with the starting winding as shown in diagram above.
As a capacitor draws leading current , therefore, Is leads V, this increases the phase between the two currents and therefore Sin α is increased and therefore starting torque,Tst = KIsImSinα is increased.
Therefore, these motors are used in applications where high starting torque is required e.g compressors, large fans, water pumps, drilling machines etc.
When the motor attains about 75% of synchronous speed, the centrifugal switch opens and the capacitor and the starting winding are disconnected. The motor continues to run as a single phase induction motor.
65. A solar cell is a ____ transducer.
Explain:- Active transducers:
1.Active transducers are those which do not require any power source for their operation.
2.They work on the energy conversion principle. They produce an electrical signal proportional to the input (physical quantity).
3.Piezoelectric, thermocouple, and photovoltaic cell transducers are some examples of active transducers.
Passive transducers:
1.Transducers which require an external power source for their operation is called a passive transducer.
2.They produce an output signal in the form of some variation in resistance, capacitance, or any other electrical parameter, which then has to be converted to an equivalent current or voltage signal.
3.LVDT is an example of a passive transducer. LVDT is used as an inductive transducer that converts motion into an electrical signal.
4.Thermistor and the photoconductive cell is an example of passive transducer."
66. The value of load factor should be ____ for more saving in electrical energy.
Explain:- Load factor (Lf):
The load factor is the ratio of the average load power to the maximum demand in a specific period of time.
It can also be defined as the ratio of the total energy used over a specific period of time (KWh) to the total possible energy available within that period (i.e., Maximum demand over that period)
Load factor value is between 0 and 1.
The high value of the load factor means the load is using electrical energy more efficiently.
Hence, the high load factor gives more savings of electrical energy, which means the cost of power generation will be lower.
Diversity factor (Divf):
It is defined as the ratio of the sum of the maximum demand of individual loads of the system to the maximum demand of the system itself.
The diversity factor is always greater than 1.
By increasing the individual peak loads, the diversity factor will be increased.
The load is using electrical energy more efficiently and the system efficiency also increases.
So, the cost of power generation also decreased because of increasing power generation.
Hence, the Load factor and the Diversity factor values should be high to lower the cost of power generation.
67. Load factor can be improved by which of the following ?
Explain:- 1.What is Load factor in power systems?
Ans Load factor is a measure of how effectively a power system is utilized over a specific period of time.It is the ratio of the average load over a given time period to the peak load during that period.Load Factor incdicates how close the actual load is to the peak load and a higher load factors means the system is being utilized efficiently.
2. How can Load Factor be improved in power systems ?
Ans Load Factor can be improved in power systems by implementing load management techniques such as load shedding,demand response, and energy conservation measures.these techniques help in reducing the peak load and spreading the load evently throughout the day.By minimizing the difference between the average load and the peak load,the load Factor can be increased.
69. N no. of traditional bulbs are replaced by LEDs in a building. The cost of each LED is P rupees. The saving in energy by using LEDs is X units per annum. The tariff rate is T rupees per unit. What is the payback period ?
Explain:- To calculate the payback period when replacing traditional bulbs with LEDs, we compare the initial investment with the annual savings from reduced energy consumption.
N = Number of LEDs installed
P = Cost of each LED (in ₹)
X = Annual energy saving per LED (in units)
T = Tariff rate (₹ per unit of electricity)
Total cost is the number of LEDs multiplied by the cost per LED.
Total Cost=𝑁×𝑃
Annual savings is the energy saved multiplied by the tariff rate.
Annual Savings=X×T
Payback Period=Total Cost/Annual Savings
Payback Period=NP/XT
70. Which of the following methods can be used for power factor improvement ?
Explain:- Low power factor in a system arises from unavoidable inductive loads consisting of lighting fixtures, motors, transformers, electromagnets etc. The way to improve power factor and go for better utilization of generation and distribution facilities involves the following—
1.Use of more efficient motors with high power factor.
2.Select optimum sizes of equipment/ motors. They have high power factor at optimum loads.
3.Connect capacitors of suitable rating across motor terminals.
4.Energy efficient lighting plus separate capacitors for lighting load
5.Use shunt capacitors/ KVAR panels / APFC panels
6.Capacitors with all welding machines
7.Capacitors/ APFC panels at substation
8.FACTS systems st suitable locations .
9.Series capacitors in transmission lines
10.Use of synchronous generators to provide leading currents
71. An ac voltage can be converted into a unidirectional voltage by using
Explain:- A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (or voltage), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (or voltage), which is unidirectional.
72. An ideal current source is one whose internal resistance is
Explain:- Ideal voltage source: An ideal voltage source have zero internal resistance.
Practical voltage source: A practical voltage source consists of an ideal voltage source (VS) in series with internal resistance (RS) as follows.
An ideal voltage source and a practical voltage source can be represented as shown in the figure. Ideal current source: An ideal voltage source has infinite resistance. Infinite resistance is equivalent to zero conductance. So, an ideal current source has zero conductance.
Practical current source: A practical current source is equivalent to an ideal current source in parallel with high resistance or low conductance. Ideal and practical current sources are represented as shown in the below figure
73. Avalanche breakdown in a semiconductor diode occurs when
Explain:- Break down of a diode usually occurs in the reverse biased state. Under the reverse biased state of a PN diode, the positive end of the battery is connected to the n-side of the diode and the negative end is connected to the p-side of the diode. As an outcome of this, electrons will be drawn in respect to the off-side and the holes will be drawn in respect to the side of the p-side. There are two types of breakdown that happen in a diode. They are Zener breakdown and Avalanche breakdown. Zener diode:
The phenomena of Zener breakdown that happens in a pn junction diode of heavy doping and a thin junction, that is in a way that the size of the depletion layer is very small. Zener breakdown is not that the diode is damaged. As the current is only because of drifting of electrons, there are certain limitations to the increase in current.
Avalanche breakdown: The phenomenon of Avalanche breaks down that happens in a pn junction diode which is averagely doped that has the thickest junction, that is the thickness of the depletion section is high. This phenomenon normally takes place when there is a greater reverse voltage. Which is evidently greater than that of the Zener breakdown voltage. That is when we increase the applied reverse voltage, the electric field over the junction will keep on rising.
Therefore, Avalanche breakdown in a diode occurs when the reverse bias exceeds a certain value.
74. The input and output signals of a common-emitter amplifier are
Explain:- Leading Phase
1.The phase of a decoupled emitter resistor in a circuit changes when the signal frequency is low enough so that the value of the emitter resistor can be compared to the reactance of the capacitor.
2.A leading phase shift is observed during this transition.
3.Therefore, the phase shift will be less than 180 degree.
4.This is because the gain falls to a value that is dependent on the value of the emitter resistors and the collector load.
Lagging Phase 1.There will be effects at the top of the frequency from the capacitance of the collector-base junction and the parasitic capacitance.
2.This is always voltage-dependent or Miller capacitance.
3.Therefore, a lag is observed and the phase shift is greater than 180 degree.
4.This will be asymptotic to 90 degree
Hence, in the common emitter amplifier, the relationship between the phase of the input and output signals is 180 degree.
NOTE
-An input characteristic is a curve between base current and base emitter voltage at constant collector emitter voltage.
-An output characteristic is the curve between collector current and collector-emitter voltage at constant base current.
-An amplifier is a device that increases the amplitude of an AC signal. and this process is called amplification.
75. In a amplifier, the coupling capacitors are used
Explain:- Coupling capacitors are essential components in amplifier circuits. They are used to prevent interference of a transistor's bias voltage by AC signals.
OR
The coupling capacitors in an amplifier prevent dc mixing with input and output . These capacitors block unwanted dc components and decouple or isolate dc from input and output.
76. One of the effects of negative feedback in amplifiers is to
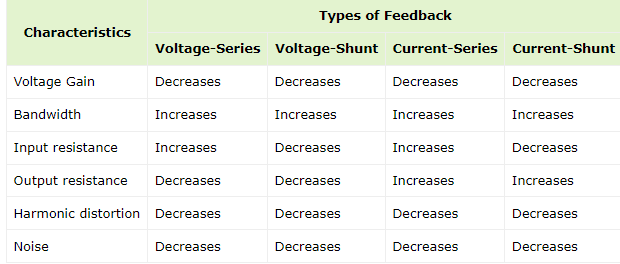
Explain:- An Amplifier is simply an electronic device that is used to increase the strength of the input signal. In this process of amplification, even the disturbances or noise present in the input signal also get amplified.
That’s the reason why we use negative feedback in amplifiers, a portion of the output signal in a phase opposite to the input signal is fed to the input of the amplifier which significantly reduces the noise level in the output signal.
Negative feedback in amplifiers has the following advantages: 1. Stabilizes Amplifier Gain
2. Reduces Non-linear Distortion
3. Increases Circuit Stability
4. Increases Input Impedance/Resistance
5. Decreases Output Impedance/Resistance
6. Reduces Noise Level
7. Improves Frequency Response and Bandwidth
8. More Linear Operations
77. The negative feedback in amplifier
Explain:- Negative feedback reduces gain of the amplifier. It also reduce distortion, noise and instability. This feedback increases bandwidth and improves input and output impedances. Due to these advantages, the negative feedback is frequently used in amplifiers.
79. The attenuator in a signal generator is used to
Explain:- Attenuate the input signal amplitude without altering the frequency contents Attenuators are passive devices which are used to weaken or attenuate the high-level output of a signal generator. In measuring signals, attenuator pads or adapters are used to lower the amplitude of the signal a known amount to enable measurements, or to protect the measuring device from signal levels that might damage it. While attenuating, the frequency remains unaltered.
80. A gate is enabled with when its enable input is at logic 1. The gate is
Explain:- The output of AND gate is high when all inputs are high and output of AND gate is low when any one of the inputs is low. NAND gate output is low when all inputs are high and output of NAND gate is high only when at least one of input is low. Therefore, NAND gates and AND gates are enable when its enable input is logic ‘1’.
81. The maximum number of 3-input gate in a 16 pin 1C will be
Explain:- To find the maximum number of 3-input logic gates that can be implemented in a 16-pin IC, we need to account for the pins used by each gate and for power supply.
Assumptions:
The IC uses 2 pins for power supply: Vcc and GND.
So, available pins for I/O = 16 − 2 = 14 pins.
Each 3-input logic gate typically requires:
3 input pins
1 output pin
So, 4 pins per gate
Now, calculate how many 3-input gates can fit: Max number of gates= 14/4= 3 gates.
82. HTL is a modified form of
Explain:- Yes, high-threshold logic (HTL) is a modified form of transistor-transistor logic (TTL). HTL is a variant of diode–transistor logic that's used in environments with high noise. HTL is also known as low-speed logic (LSL) or high-level logic (HLL).
83. The radix of hexadecimal number system is
Explain:- Octal Number System: The octal number system has only eight (8) digits from 0 to 7. Every number (value) represents with 0,1,2,3,4,5,6 and 7 in this number system. The base or radix of the octal number system is 8 because it has only 8 digits.
Binary Number System: A Binary number system has only two digits that are 0 and 1. Every number (value) represents 0 and 1 in this number system. The base or radix of the binary number system is 2 because it has only two digits.
Decimal number system: The decimal number system has only ten (10) digits from 0 to 9. Every number (value) represents with 0,1,2,3,4,5,6, 7,8 and 9 in this number system. The base or radix of the decimal number system is 10 because it has only 10 digits.
Hexadecimal number system: A Hexadecimal number system has sixteen (16) alphanumeric values from 0 to 9 and A to F. Every number (value) represents with 0,1,2,3,4,5,6, 7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E and F in this number system. The base or radix of the hexadecimal number system is 16 because it has 16 alphanumeric values.
84. The octal equivalent of the Binary number 11010111 is
Explain:- (11010111)2 = (327)8
Step by step solution
Step 1: Write down the binary number
(011010111)2
Group all the digits in sets of three starting from the LSB (far right). Add zeros to the left of the last digit if there aren't enough digits to make a set of three.
011 010 111
Step 2: Use the table below to convert each set of three into an octal digit. In this case,
011=3, 010=2, 111=7. So, the number 327 is the octal equivalent to 11010111 in binary.
85. Universal Register
Explain:- 1. A Universal shift register is a register have both shifts and parallel load capabilities.
2.Universal shift registers are used as memory elements in computers.
3.These are capable of transferring/shifting the data either towards the right or left in serial and parallel modes.
4. Based on the mode of input/output operation,univerisal register can perform shift operation in the following ways:
1. Serial IN-Serial OUT(SISO)
2. Serial IN-Parallel OUT (SIPO)
3.Parallel IN-Parallel OUT (PIPO)
4. Parallel IN-Serial OUT (PISO)
86. A ring-counter consists of five FLIP-FLOPS will have
Explain:- A Straight ring counter with 'n' flip-flops will have n states. Therefore, the ring counter with 5 flip-flops will have 5 states. A Johnson counter is a modified ring counter, where the inverted output from the last flip flop is connected to the input to the first. The MOD of johnson counter is 2n if n flip flop is used.
87. A memory has 16-bit address bus. The number of locations in this memory are
Explain:- Memory location for 16 bit = 216 = 65,536 = 64 K
88. A memory in which the contents get erased when power failure occurs is
Explain:- Random Access Memory (RAM):It is volatile, which means if a power failure occurs or the computer is turned off, the information stored in RAM will be lost. All data stored in computer memory can be read or accessed randomly at any time.
Read-Only Memory (ROM):It is a non-volatile memory; it means that the stored information cannot be lost even when the power is turned off or the system is shut down.
89. The instruction set of a microProccesor
Explain:- An Instruction is a command given to the computer to perform a specified operation on given data. The instruction set of a microprocessor is the collection of the instructions that the microprocessor is designed to execute.
90. The number of interrupts in 8085 microProccesor is
Explain:- Interrupts are the signals generated by the external devices to request the microprocessor to perform a task. There are 5 interrupt signals, i.e. TRAP, RST 7.5, RST 6.5, RST 5.5, and INTR.
Interrupt are classified into following groups based on their parameter
− Vector interrupt − In this type of interrupt, the interrupt address is known to the processor. For example: RST7.5, RST6.5, RST5.5, TRAP.
Non-Vector interrupt − In this type of interrupt, the interrupt address is not known to the processor so, the interrupt address needs to be sent externally by the device to perform interrupts. For example: INTR.
Maskable interrupt − In this type of interrupt, we can disable the interrupt by writing some instructions into the program. For example: RST7.5, RST6.5, RST5.5.
Non-Maskable interrupt − In this type of interrupt, we cannot disable the interrupt by writing some instructions into the program. For example: TRAP.
Software interrupt − In this type of interrupt, the programmer has to add the instructions into the program to execute the interrupt. There are 8 software interrupts in 8085, i.e. RST0, RST1, RST2, RST3, RST4, RST5, RST6, and RST7.
Hardware interrupt − There are 5 interrupt pins in 8085 used as hardware interrupts, i.e. TRAP, RST7.5, RST6.5, RST5.5, INTA.
92. Cost of operation of which plant is least ?
Explain:- The operating or running cost is a variable factor-dependent mainly on the amount of energy generated. It includes fuel cost, operating labor cost, maintenance cost, supplies, supervision, operating taxes, etc.
Some of these costs remain constant as long as the plant is in active operation or is held in readiness to produce energy. The operating cost and its contributing factors also vary with the type of power plant.
In thermal power plants, the major contributing factor in total operating cost id the cost of fuel, which may be 75% of the total operating cost.
In Nuclear power plants, fuel costs are lower but operation and maintenance cost is much more than a conventional thermal; plant.
The operating cost of a hydroelectric plant is considerably less due to the absence of the fuel cost.
93.A Francis turbine is
Explain:- A.Impulse Turbine: If at the inlet of the turbine, the energy available is only kinetic energy, the turbine is known as impulse turbine. e.g. a Pelton wheel turbine.
B. Reaction Turbine: If at the inlet of the turbine, the water possesses kinetic energy as well as pressure energy, the turbine is known as a reaction turbine. e.g. e Francis and Kaplan turbine.
C. Tangential flow turbines: In this type of turbine, the water strikes the runner in the direction of the tangent to the wheel. Example: Pelton wheel turbine
Radial flow turbines: In this type of turbine, the water strikes in the radial direction. accordingly, it is further classified as
1.Inward flow turbine: The flow is inward from periphery to the centre (centripetal type); Example: old Francis turbine
2.Outward flow turbine: The flow is outward from the centre to periphery (centrifugal type); Example: Fourneyron turbine
3.Axial flow turbine: The flow of water is in the direction parallel to the axis of the shaft. Example: Kaplan turbine and propeller turbine
Francis turbine is a radial inward flowing reaction turbine.
94. Load factor during a period is
Explain:- The load factor is also the ratio of the number of units generated in a given period to the number of units that could have been generated with the same maximum demand.
The load factor is always less than one because maximum demand is never lower than average demand. A high load factor indicates that the load is using the electric system more efficiently. A low load factor means that power usage is occasionally high.
95. Identify the incorrect relation.
Explain:- The Cosine of angle between Current and Voltage is called Power Factor.
1.P = VI Cosθ
2.Cosθ = P ÷ V I
3.Cosθ = kW ÷ kVA
4.Cosθ = True Power ÷ Apparent Power
The ratio between Active Power and Apparent Power in volts-amperes is called power factor.
1.Cosθ = Active Power ÷ Apparent Power
2.Cosθ = P ÷ S
3.Cosθ = kW ÷ kVA
Where kW = P = Real Power in kilo-Watts
kVA = S = Apparent Power in kilo-Volt-Amperes or Watts
Cosθ = Power factor
96. A diesel power plant is best suited as
Explain:- Diesel power plants are best suited as standby power plants. They are also known as standby power stations.
Diesel power plants are used in many applications, including:
1.Providing standby power during emergencies
2.Supplying electricity in remote areas
3.Serving as a primary source of power in locations where grid connectivity is limited
4.Supplying hospitals, telephone exchanges, radio stations, cinema theaters, and industries
5.Mobile power generation
6.Transportation systems such as automobiles, railways, air planes, and ships
Diesel power plants are compact and can be located where they are needed. They can produce limited amounts of electrical energy. Diesel electric power plants can range from 1 MW to 50 MW capacity. Diesel engines have an efficiency of about 35%.
97. In overload transmission lines, the effect of capacitance can be neglected when the length of the line is less than
Explain:- Capacitance in Overhead Transmission Lines:
Transmission lines have inductance and capacitance due to the distributed nature of the line. The inductance of the line is responsible for the magnetic field that surrounds the conductor, while the capacitance is due to the electric field between the conductor and the ground. The capacitance of a transmission line is proportional to the length of the line, the spacing between the conductors and the distance from the conductors to the ground.
Effect of Capacitance:
Capacitance causes a voltage drop in the line, which is proportional to the current flowing through it. This voltage drop is called the charging current and is due to the charging and discharging of the capacitance. The charging current is in phase with the voltage, which means that it does not cause any power loss. However, it can cause voltage regulation problems and can lead to overvoltage conditions.
When the length of the line is very long, the effect of capacitance becomes significant and needs to be taken into account. The capacitance of the line causes the voltage to be reduced, which can lead to power losses and voltage regulation problems. Therefore, it is essential to consider capacitance when designing long transmission lines.
When the length of the line is short, the effect of capacitance can be neglected. This is because the voltage drop due to capacitance is small compared to the voltage drop due to resistance and inductance. Therefore, for short transmission lines, the effect of capacitance can be ignored, and only the resistance and inductance need to be taken into account.
Conclusion: In overhead transmission lines, the effect of capacitance can be neglected when the length of the line is less than 80 km. Beyond this distance, the effect of capacitance becomes significant and needs to be taken into account when designing the transmission line.
98. Presence of ozone as a result of corona is harmful because
Explain:- When an alternating potential difference is applied across two conductors whose spacing is large as compared to their diameters, there is no apparent change in the condition of atmospheric air surrounding the wires if the applied voltage is low.
When the applied voltage exceeds a certain value (critical disruptive voltage), the conductors are surrounded by a faint violet glow called corona.
It can be detected by hissing sound, faint luminous and presence of ozone which is detected by odour. The presence of ozone is harmful because it corrodes the material.
99. ACSR conductor implies
Explain:- Aluminium conductor steel-reinforced cable (ACSR) is a type of high-capacity, high-strength stranded conductor typically used in overhead power lines. The outer strands are high-purity aluminium, chosen for its good conductivity, low weight, low cost, resistance to corrosion and decent mechanical stress resistance.
100. Ten discs usually suggest that the transmission line voltage is
Explain:- Each disc insulator is rated for about 11 kV to 12 kV (depending on design and safety margins). However, due to environmental factors and safety considerations, more discs are often used.
Line Voltage≈Number of Discs×11 to 12 kV
10 discs ≈ 110 to 120 𝑘 𝑉 ( 𝑙 𝑖 𝑛 𝑒 − 𝑡 𝑜 − 𝑛 𝑒 𝑢 𝑡 𝑟 𝑎 𝑙 ) , or about 132 kV (line-to-line) 10 discs≈110 to 120kV(line−to−neutral), or about 132 kV (line-to-line)
Ten discs usually suggest a transmission line voltage of approximately 132 kV.
101. Isolators are used to disconnect the circuit when
Explain:- Use of Isolators in Electrical Circuits
Definition of Isolators: Isolators are switching devices that are used to disconnect a circuit from the source of power, and this disconnection is done when the circuit is not in operation.
Uses of Isolators:
Isolators are used in electrical circuits for various reasons. Some of the significant reasons are:
1. To provide safety to the workers: Isolators are used to disconnect the circuit when the circuit is not in operation. This disconnection ensures the safety of the workers who are working on the circuit.
2. To provide safety to the equipment: Isolators are used to disconnect the circuit from the source of power when the circuit is not in operation. This disconnection ensures the safety of the equipment that is connected to the circuit.
3. To provide easy maintenance: Isolators are used to disconnect the circuit from the source of power when the circuit is not in operation. This disconnection allows for easy maintenance of the equipment that is connected to the circuit.
When to use an Isolator:
An isolator should be used when:
- The circuit needs to be disconnected from the source of power.
- The circuit needs to be disconnected for maintenance purposes.
- The circuit needs to be disconnected for safety reasons.
Importance of Isolators:
The importance of isolators in electrical circuits can be understood from the following points:
- Isolators provide safety to the workers who are working on the circuit.
- Isolators provide safety to the equipment that is connected to the circuit.
- Isolators allow for easy maintenance of the equipment that is connected to the circuit.
- Isolators help in preventing accidents that can occur due to electrical faults.
Answer to the given question:
The correct answer to the given question is option 'D'.
Isolators are used for disconnecting a circuit when the line carries no current. This is because the isolator is a switching device that disconnects the circuit from the source of power when the circuit is not in operation. Therefore, the circuit should not be carrying any current when the isolator is used to disconnect the circuit from the source of power.
102. The sag of the conductors of the transmission line is 1.5 m when the span is 100 m. Now if the height of the supporting towers is increased by 20%, the sag will
Explain:- The sag is given by
S=WL2/8T
Where w is the weight per unit length of the conductor
T is the tension of the conductor
L is the length of the span
Here in the question height of the supporting towers is increased by 20 % which independent to sag. Hence there will be no change in sag.
104. SF6 gas
Explain:- Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) has many properties, including:
Physical: Colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and non-flammable
Chemical: Non-polar, organic, and chemically stable
Thermal: Temperature-resistant up to 500°C and has high thermal conductivity
Electrical: Excellent dielectric properties and arc quenching properties
Electronegative: Free electrons are easily removed from discharge by the formation of negative ions
Recombination: Has a unique property of fast recombination after the source energizing spark is removed
SF6 is also strongly electronegative and has an atmospheric lifetime of 800–3200 years.
105. Which of the following contact point metals has the highest melting point ?
Explain:- Tungsten (W) has the highest melting point of all metals, at 3,410 °C (6,170 °F). It also has the highest boiling point of all metals, at 6,203 K.
Here are the melting points of some other common metals:
1.Aluminum: 660°C (1220°F)
2.Brass: 930°C (1710°F)
3.Chromium: 1860°C (3380°F)
4.Copper: 1084°C (1983°F)
5.Gold: 1063°C (1945°F)
6.Cast Iron: 1204°C (2200°F)
7.Lead: 328°C (622°F)
8.Nickel: 1453°C (2647°F)
106. The basic function of circuit breaker is to
Explain:- The Function of Circuit Breaker
A circuit breaker is an essential component in an electrical system that is designed to protect the circuit and its components from damage caused by excessive current. It acts as a safety device and is commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. The primary function of a circuit breaker is to safeguard the circuit from overloads, short circuits, and ground faults, ensuring the safety of the electrical system and preventing potential hazards.
1. Safeguarding the Circuit
The main function of a circuit breaker is to protect the circuit from overloading. When the current flowing through the circuit exceeds the rated capacity of the wires, it can cause overheating and potentially lead to a fire. The circuit breaker detects this excessive current and quickly interrupts the circuit, preventing further flow of electricity and preventing damage to the wires and other components.
2. Detecting Short Circuits
Short circuits occur when there is a direct connection between the live and neutral wires or between the live wire and the ground. This can happen due to faulty wiring, damaged insulation, or equipment failure. In such cases, the current flowing through the circuit becomes extremely high, posing a significant risk of fire and electrical shock. The circuit breaker detects the sudden surge in current and trips, effectively isolating the faulty section of the circuit and preventing further damage.
3. Ground Fault Protection
A ground fault occurs when the live wire comes into contact with a conductive surface, such as a metal appliance or a water pipe. This can happen due to insulation failure or faulty equipment. Ground faults can be extremely dangerous, as they can lead to electric shocks and electrocution. Circuit breakers equipped with ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) are used to detect these faults and quickly interrupt the circuit, protecting individuals from electrical hazards.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary function of a circuit breaker is to safeguard the circuit by detecting and interrupting excessive current flow caused by overloads, short circuits, and ground faults. By doing so, circuit breakers play a crucial role in preventing fires, electrical damage, and potential harm to individuals.
107. Unit of solid angle is
Explain:- Steradian:
It is defined as the solid angle of a sphere subtended by a portion of the surface whose area is equal to the square of the sphere’s radius.
Radian:
A unit of measurement of angles equal to about 57.3°, equivalent to the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius.
Solid angle:
A three-dimensional analog of an angle, such as that subtended by a cone or formed by planes meeting at a point. It is measured in steradian.
Plane angle:
An angle that for a given dihedral angle is formed by two intersecting lines each of which lies on a face of the dihedral angle and is perpendicular to the edge of the face.It is measured in radian
108. Which locomotive has the highest operational availability ?
Explain:- Electric locomotives have the highest operational availability. They require less maintenance and repairs than steam locomotives and can be kept in service for 95% or more.
Electric traction is locomotion where the driving force comes from electric motors. It's used in electric trains, tramcars, trolley buses, and diesel-electric vehicles.
Electric locomotives with hydroelectric power plants are the most efficient. Steam locomotives have an efficiency of 5-7%, while gas turbine electric locomotives have an efficiency of 10%.
109. In gas welding the gases used are
Explain:- The correct answer is Oxygen and acetylene.
Key Points:
1.Gases used in welding are Oxygen and acetylene.
2.Oxy-acetylene welding is a very common welding process.
3.In oxy-acetylene welding, the flame produced by the combination of the gases melts the metal faces of the workpieces to be joined, causing them to flow together.
4.Because steel melts at a temperature above 1,500 oC, the mixture of oxygen and acetylene is used as it is the only gas combination with enough heat to weld steel.
Additional Information
1.As acetylene is lighter than air, there are rare chances of them accumulating at low levels.
2.This property makes it safe to use in any processing facility or in underground applications.
3.Oxy-acetylene is well-known for its flexibility and is suited for various machining operations other than welding, such as brazing, cutting, etc.
4.Acetylene is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne.
5.The chemical formula is C2H2.
6.It is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block.
7.Acetylene is formed by any of three methods: by the reaction of water with calcium carbide, by passing through an electric arc of a hydrocarbon, or by partial combustion of methane with air or oxygen.
110. Eyes of welding operator must be protected against
Explain:- 1.Welding arcs give off radiation over a broad range of wavelengths - from 200 nm (nanometers) to 1,400 nm (or 0.2 to 1.4 µm, micrometers).
2.This includes ultraviolet (UV) radiation (200 to 400 nm), visible light (400 to 700 nm), and infrared (IR) radiation (700 to 1,400 nm).
3.This is the reason that eyes need to be protected against both UV and Infra-Red rays.
111. Flux used in TIG welding is
Explain:- Flux is mainly used for the following purposes
1.It prevents the oxidation of the surface of the weld which can contaminate the welded portion. (Metals at high-temperature forms oxides which results in the poor surface)
2.It helps in forming an alloy at the welded portion which improves the strength.
3.In arc welding, the flux coating helps in directing the spark that’s why the electrode is kept concave in shape so that spark can be precisely directed towards the cavity where welding has to be performed.
Flux is not required in TIG since the inert gas envelope protects the molten metal without forming oxides and nitrates so the weld is smooth, uniform, and ductile.
Hence, tungsten arc welding produces very clean welds. No cleaning or slag removal is required because no flux is used.
112. Which method is appropriate for heating non-ferrous metals ?
Explain:- Induction heating is a method that can be used to heat non-ferrous metals. It involves heating electrically conductive materials, such as metals and semiconductors, using electromagnetic induction.
Induction heating is used in a variety of applications, including:
1.Melting precious metals and their alloys
2.Melting other pure non-ferrous metals and alloys
3.Heat treating
4.Soldering
5.Preheating for welding
Induction furnaces are often used to melt non-ferrous metals, such as copper, brass, and aluminum. They offer several advantages, including:
1.Fast heating speed
2.Low cost
3.Environmental protection
4.Low noise
5.Easy maintenance
6.High efficiency
7.Energy-saving
8.Long use life
113. Piezoelectric materials serve as a source of
Explain:- Piezoelectric materials can be a source of ultrasonic waves.
Piezoelectric materials can also produce an electric voltage when they are stressed. This can be caused by bending, stretching, or vibrations. This property allows for the implementation of renewable and sustainable energy.
114. Bronze is an alloy of
Explain:- Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin.
Modern bronze is typically 88% copper and 12% tin. The addition of other elements can affect the hardness, ductility, flexibility, and other properties of bronze. Compared to pure copper, bronze is stronger, harder, more corrosion-resistant, and easier to cast.Bronze is commonly used for bearings, bushings, springs, and similar fittings.
115.The unit of retentivity is
Explain:- The retentivity of a material is its capacity to remain magnetized even after the external magnetizing field has removed. Therefore, the material used in temporary magnets should have low retentivity, so that it doesn't get magnetized, or gets demagnetized easily.
The unit of retentivity is Weber/Metre2
116. Which of the following is a Diamagnetic substance ?
Explain:- Diamagnetic Substances: The substances which are weekly magnetized when placed in an external magnetic field, in a direction opposite to the applied field are called diamagnetic substances.
Example: Copper, lead, gold, silver, zinc, antimony, bismuth, etc. Properties: These substances are repelled by a magnet.
OR
Diamagnetic substance:
1.Diamagnetic substances are those substances which are repelled by a magnet.
2.From microscopic point of view, these are the substances whose atomic orbitals are completely filled.
3.The cause of magnetization for these substances is the orbital motion of electron in which velocity of the electron is affected by the external magnetic field.
4.Some examples of diamagnetic substances are antimony, bismuth, graphite, copper, lead, gold, silver, zinc, quartz, mercury, alcohol, sodium chloride, water, hydrogen, air, argon etc.
5.Two of the strongest diamagnetic materials are graphite and bismuth.
Properties of diamagnetic substances:
1.When placed in a non-uniform magnetic field, it tends to move from stronger to weaker regions of the magnetic field.
2.A diamagnetic rod when placed in a uniform magnetic field, the rod aligns itself in a direction perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field.
3.The permeability of a diamagnetic substance is less than one.
4.When it is placed in a magnetic field, it develops weak magnetization in a direction opposite to the direction of the magnetizing field.
5.As soon as the magnetizing field is removed, it loses its magnetization.
6.The magnetic susceptibility does not depend upon temperature. It has a small negative value.
117. Earth tester is type of meter
Explain:- Yes, an earth tester is a type of ohmmeter. It's also known as an earth resistance meter or ground resistance tester. Earth testers measure earth resistance. They work on the principle of Ohm's law, and don't require the user to disconnect the ground system. Earth testers can measure earth resistance in both grounded and ungrounded systems. They can also measure cable resistances and continuity across wires and circuit breakers. When choosing an earth tester, you can consider factors like: Soil composition, Moisture content, Temperature, Sun exposure.
EXTRA INFORMATION
118. Which of the following properties of refrigerant is undesirable ?
Explain:- Desirable Properties of a Refrigerant:
Low boiling point
High latent heat of vaporization
Low specific volume
Non-toxic and non-flammable
Low viscosity
High thermal conductivity
Chemically stable
Environmentally friendly (low ODP and GWP)
Moderate operating pressures
Undesirable Properties Include:
High toxicity
High flammability
High ozone depletion potential (ODP)
High global warming potential (GWP)
High boiling point(which reduces cooling effectiveness)
High specific volume (requires larger compressors)
Corrosiveness
High viscosity (causes pressure drops)
119. If d is the distance of a surface from a source, the illumination upon the surface will vary as
Explain:- The illumination upon the surface will vary as 1/d2. This is known as the inverse square law. It states that the light intensity decreases as the square of the distance from the source increases. This is because the light is spread out over a larger area as it travels further from the source.
120. A merz prize protection is suitable for
Explain:- Merz-Price protection is used to protect transformers and generators/alternator. Note: Merz-Price protection is used to protect both transformer and alternator but if we have to choose any one option among these two, then the alternator will be the best answer.