1. The resistance of a wire is R ohms. It is stretched to double its length, the new resistance of the wire in ohms is
Explain:- R = ρL/A When L is doubled , As we know that the volume of the wire remains same.
old volume = new volume AL = A'L' ....(1) ( as volume = area x length )
L' = 2L So, from (1) A' = A/2
So the new resistance is , R' = ρL'/A'
or R' = ρ(2L)/(A/2) = 4 (ρL/A) => R' = 4R
2. A 10 m long wire of resistance 20 ohms is connected in series with a battery of e.m.f. 3V (negligible internal resistance) and a resistance of 10 ohms. The potential gradient along the wire in volt per metre is
Explain:-
3. A 200 W and 100 W bulb both meant for operation at 220 V are connected in series. When connected to a 220 V supply, the power consumed by them will be
Explain:-
4. Three 2 ohms resistances are connected to form a triangle, the resistance between any two corners is
Explain:-
5. Two heater wires of equal length are first connected in series and then in parallel. The ratio of heat produced in the two cases will be
Explain:-
6. How much electrical energy in kWh is consumed in operating ten 50 W bulbs for 10 hrs in a day in a month of 30 days ?
Explain:-
7. The force between the plates of a parallel plates capacitor of capacitance C and distance of separation of plates d with a potential difference V between the plates is
Explain:-
9. Magnetic flux passes more readily through
Explain:- Magnetic flux passes more readily through a material with high permeability. Permeability is a measure of how much a material can become magnetized. Materials with high permeability, such as iron, allow magnetic field lines to pass through more easily, resulting in a higher magnetic flux. On the other hand, materials with low permeability, such as air or vacuum, offer greater resistance to the passage of magnetic field lines, leading to lower magnetic flux. Therefore, magnetic flux passes more readily through materials with high permeability.
10. The unit of pole strength is
Explain:- The unit of pole strength is the ampere-meter (A-m). This is the standard unit in the MKS (meter-kilogram-second) system, as well as in the SI (International System of Units). The pole strength of a magnet is a measure of its ability to attract other magnetic materials towards itself and is represented by the product of the current (in amperes) and the distance (in meters) from the center of the magnet. Therefore, the unit of pole strength is the ampere-meter (A-m)
11. M.M.F. in a magnetic circuit corresponds to _______ of an electric circuit
Explain:- The M.M.F. (magnetomotive force) in a magnetic circuit corresponds to the voltage of an electric circuit. Just as voltage is the driving force that causes current to flow in an electric circuit, M.M.F. is the driving force that causes magnetic flux to establish in a magnetic circuit. It is analogous to the voltage in an electric circuit and is measured in ampere-turns (AT) or ampere-meters (A-m)
12. The B-H curve of ________ will not be straight line
Explain:- The B-H curve of a ferromagnetic material will not be a straight line. The B-H curve, also known as the magnetization curve or hysteresis loop, is a graphical representation of the relationship between the magnetic field strength (H) and the magnetic flux density (B) of a ferromagnetic material. The curve shows that for a given ferromagnetic material, the path traced during magnetization and demagnetization are not the same. The B-H curve of a ferromagnetic material is characterized by a nonlinear relationship between H and B, and exhibits hysteresis, which means that the magnetic flux density lags behind the magnetic field strength. Therefore, the B-H curve of a ferromagnetic material will not be a straight line. Examples of ferromagnetic materials include:
1.Iron
2.Cobalt
3.Nickel
4.Gadolinium
5.Neodymium
6.Ferromagnetic ceramics
Ferromagnetic materials are those that exhibit a spontaneous net magnetization at even in the absence of an external magnetic field. When placed in an external magnetic field, ferromagnetic materials are strongly magnetized in the direction of the field. These materials are strongly attracted to a magnet and retain their magnetization for some time. Some common examples of ferromagnetic materials are iron, cobalt, and nickel, which are all found in nature. Additionally, there are some alloys and compounds containing one or more of these elements, such as gadolinium and neodymium, which also exhibit ferromagnetic properties.
13. A current of 2A through a coil sets up flux linkages of 4 wb-turn. The inductance of the coil is
Explain:-
14. The specific gravity of electrolyte in a lead acid cell increases, the internal resistance of the cell
Explain:- When the specific gravity of the electrolyte in a lead-acid cell increases, the internal resistance of the cell decreases. The internal resistance of a lead-acid cell is mainly due to the electrolyte. As the specific gravity of the electrolyte increases, the internal resistance decreases. This is because the specific gravity of the electrolyte is directly related to the concentration of sulfuric acid in the electrolyte, which affects the conductivity of the electrolyte. A higher specific gravity indicates a higher concentration of sulfuric acid, leading to lower internal resistance. Therefore, an increase in the specific gravity of the electrolyte results in a decrease in the internal resistance of the lead-acid cell
15. The form factor of a ________ wave is 1
Explain:- The form factor of a square wave is 1.This means that the RMS (root mean square) value of the waveform is equal to its average value. For a square wave, both the RMS and average values are the same, The form factor is defined as the ratio of the RMS value to the average value of an alternating quantity (current or voltage) OR Average value: The average value is the arithmetic mean of all the instantaneous values of a waveform over one complete cycle. It is also known as the DC equivalent value of an AC waveform. For a sinusoidal wave, the average value is usually zero, as the waveform alternates between positive and negative values.
RMS value: The RMS value is a measure of the "average" value of a waveform, taking into account the squares of the instantaneous values. It is calculated by taking the square root of the arithmetic mean of the squares of the instantaneous values. The RMS value is always greater than or equal to the average value.The RMS value is often used in calculations involving power and energy, as it provides a more accurate representation of the energy transferred in a waveform.
16. When a 15 V square wave is connected across a 50 V a.c. voltmeter, it will read
17. In a LCR circuit, the voltage read at resonance across R, L and C are 40 V, 60 V and 60 V respectively then the applied voltage is
Explain:-
19. The resistance between any two terminals of a balanced delta connected load is 12 Ω. The resistance of each phase is
Explain:-
20. Three 50 Ω resistors are connected in star across 400 V, 3-phase supply. If one of the resistor is disconnected, then line current will be
22. If the current through the operating coil of a moving iron instrument is doubled, the operating force becomes
Explain:-
23. Hot wire instruments have ________ scale
Explain:- Hot Wire Instrument
The instruments which use the heating of the current for knowing their magnitude such type of instrument is known as the hot wire instrument. It work on the principle that the length of the wire increases because of the heating effect of the current flow through it. The hot wire instrument is used for both AC and DC current.
Construction of Hot Wire Instrument
The constructional features of a hot wire type instrument are shown in fig. The current to be measured is passed through a fine platinum iridium wire. The wire is stretched between two terminals.
Hot Wire Instrument
A second wire is attached to the fine wire at one end and to a terminal at the other end. A thread is attached to the second wire. This thread passes over a pulley and is fixed to a spring.
Working of Hot Wire Instrument
When the current is passes through the fine wire is gets heated up and expands. The sag of the wire is magnified and the expansion is taken up by the spring. This causes the pulley to rotate and the pointer to deflect, indicating the value of the current. The expansion is proportional to the heating effect of the current and hence to square of the RMS value of the current. Therefore, the meter may be calibrated to read the RMS value of the current.
Advantages of Hot Wire Instrument
1.The instrument is used for both AC and DC measurement.
2.Their construction is very simple and cheap.
3.The hot wire instrument is free from the stray magnetic field.
4.It is a transfer-type instrument i.e., the calibration is same for both the AC and DC measurement.
Disadvantages of Hot Wire Instrument
1.The hot wire instrument gives the slow response.
2.The instrument consumes more power.
3.The instability due to stretching the wire.
4.Non uniform scale.
24. The watt-hour meter is _______ instrument.
Explain:- The watt-hour meter is an integrating instrument. It measures the total amount of electrical energy (in watt-hours) consumed over a period of time, rather than providing an instantaneous power reading like a wattmeter. Integrating instruments record the cumulative value of a quantity, in this case, energy consumption.
25. A 100 W, 250 V bulb is put in series with a 40 W, 250 V bulb across 500 V supply. The current drawn will be
Explain:-
26. Norton’s equivalent is
Explain:- Norton's Theorem is similar to Thevenin's Theorem in that it produces an equivalent, simplified circuit. The major difference is that the equivalent circuit is composed of a current source and a parallel resistance rather than a voltage source and a series resistance like the Thevenin equivalent.
27. A 12 V Lead Acid Battery used in a car contains
28. The self-induced emf in a 0.2 H coil when a current in it is changing at the rate of 100 A/sec is
Explain:-
29. The power factor at resonance in R-L-C series circuit is
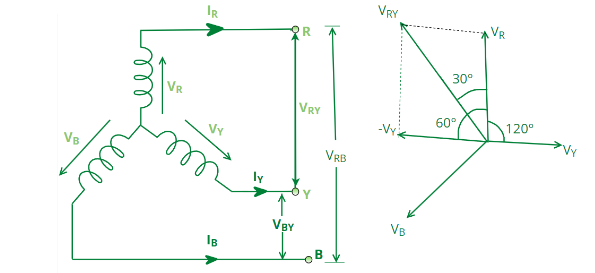
30. In a balanced three phase star connected system, the phase difference between phase voltage and their respective line voltages are
Explain:- In a balanced three-phase star connected system, the line voltage leads the corresponding phase voltage by 30 degrees. This means that the line voltage is ahead in phase compared to the phase voltage by this amount.
Phase Voltage: The voltage between each phase wire and the neutral point.
Line Voltage: The voltage between any two phase wires.
Phase Difference: In a balanced star connection, the line voltage is √3 times the phase voltage, and the line voltage leads the phase voltage by 30 degrees.
31. The number of parallel paths in the armature winding of four pole, wave connected d.c. machine having 22 coil sides is
Explain:- In a wave-connected winding, the number of parallel paths is always (2), regardless of the number of poles or coil sides.
32. A 100 kVA, 1100/400 V, 50 Hz single phase transformer has 100 turns on the secondary winding. The number of turns on its primary winding will be
Explain:- We know V1 / V2 = k = N2 / N1, Substituting 400/1100 = 100/N1, N1 = 100/400 x 1100 = 275 turns.
33. Maximum efficiency of a transformer occurs when
Explain:- A transformer's efficiency is maximized when the copper losses (losses in the windings) are equal to the iron losses (losses in the core). This occurs at a specific fraction of the full load, which varies depending on the transformer's design.
Factors Affecting Transformer Efficiency:
Output power:
As the load on the transformer increases, the efficiency generally increases, but eventually, losses become dominant.
Copper Losses: These losses are proportional to the square of the current flowing through the windings. At light loads, copper losses are low compared to iron losses. As the load increases, copper losses become more significant.
Iron Losses:
These losses, including eddy current and hysteresis losses, are primarily dependent on the core's material, frequency, and flux density. At light loads, iron losses are relatively high.
Load and Power Factor:
The efficiency is also influenced by the type of load (resistive, inductive, or capacitive) and the power factor.
Maximum Efficiency Condition:
The efficiency is maximized when the sum of copper and iron losses is minimized relative to the output power. This typically happens when the copper losses are equal to the iron losses, as shown in the figure, Testbook says.
34. A 440 V, 50 Hz three phase induction motor rotates at 1440 rpm on full load. The motor is wound for
Explain:-
35. A 5HP, 3 phase, 400 V star connected squirrel cage induction motor meant to drive a milling machine, at starting takes about
Explain:-
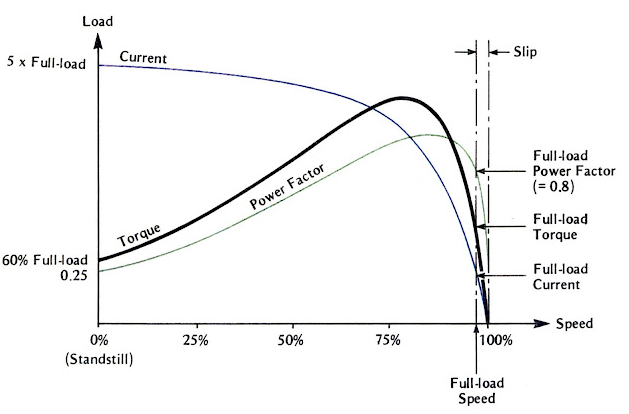
36. The torque power factor of an induction motor will be high when
Explain:- When the load on an induction motor is increased from no load to full load, both slip and power factor increase. In the low slip region torque is directly proportional to slip.
37. Synchronous motors are to be used in situations where
Explain:- Synchronous motors are ideal for situations requiring constant speed operation, high efficiency, and where power factor correction is needed. They are commonly used in industrial machinery, power generation, and applications that demand precision.
39. In alternators damper windings are used to
Explain:- The primary purpose of damper windings in alternators is to prevent hunting (oscillations) and provide starting torque for synchronous motors. They also help reduce eddy current losses and armature reaction, improving overall machine performance and stability.
Preventing Hunting:
Hunting, also known as "hunting oscillations," occurs when the rotor of a synchronous machine (like an alternator when used in a synchronous motor application) oscillates around the synchronous speed. Damper windings, being short-circuited copper bars embedded in the rotor poles, help damp these oscillations by inducing currents that resist the change in rotor position, thus stabilizing the machine's operation.
Providing Starting Torque:
Synchronous motors, unlike induction motors, are not self-starting. They require a significant external force to get them up to synchronous speed. Damper windings, with their low resistance and ability to carry current, help generate an initial torque that assists in starting the motor.
Reducing Eddy Current Losses:
The damper winding can also help reduce eddy current losses in the rotor core, which can improve the machine's efficiency.
Reducing Armature Reaction:
Armature reaction, the effect of the armature winding's flux on the main field flux, can be mitigated by the damper winding, further improving machine performance.
40. The direction of rotation of an ordinary shaded pole single phase induction motor
Explain:- The direction of rotation for a shaded pole motor is from the main (unshaded) pole to the shaded pole. The shaded pole is a copper ring or band that partially covers a pole, creating a delayed magnetic field that, along with the main field, generates the rotating magnetic field needed for the motor to start and run.