1.Superposition theorem is essential based on the concept of
Explain:- Superposition theorem =“In any linear and bilateral network or circuit having multiple independent sources, the response of an element will be equal to the algebraic sum of the responses of that element by considering one source at a time.”
Limitations of Superposition Theorem
1. The theorem does not apply to non-linear circuits. The requisite of linearity indicates that the superposition theorem is only applicable to determine voltage and current but not power. Power dissipation is a nonlinear function that does not algebraically add to an accurate total when only one source is considered at a time.
2. The application of the superposition theorem requires two or more sources in the circuit.
2.superposition theorem be applied only to
Explain:- Superposition theorem =“In any linear and bilateral network or circuit having multiple independent sources, the response of an element will be equal to the algebraic sum of the responses of that element by considering one source at a time.”
3. The superposition theorem is used when the circuit contains:
Explain:- Superposition theorem =“In any linear and bilateral network or circuit having multiple independent sources, the response of an element will be equal to the algebraic sum of the responses of that element by considering one source at a time.”
4. Thevenin theorem cannot be applied to
Explain:- Thevenin's theorem is a fundamental concept in circuit analysis, which states that any linear circuit with two terminals can be replaced by a single voltage source and a single series resistor.
However, this theorem has some limitations, which are discussed below.
1. Linear Circuit:
A linear circuit is a circuit in which the output response is proportional to the input signal. Thevenin's theorem can be applied to linear circuits only. A linear circuit satisfies the principle of superposition, homogeneity, and additivity. These principles are necessary for the theorem to hold.
2. Active Circuit:
An active circuit is a circuit that requires an external power source to operate. An example of an active circuit is an amplifier. Thevenin's theorem can be applied to active circuits, provided they are linear.
3. Passive Circuit:
A passive circuit is a circuit that does not require an external power source to operate. An example of a passive circuit is a resistor. Thevenin's theorem can be applied to passive circuits, provided they are linear.
4.Nonlinear Circuit:
A nonlinear circuit is a circuit in which the output response is not proportional to the input signal. Thevenin's theorem cannot be applied to nonlinear circuits. Nonlinear circuits do not satisfy the principle of superposition, homogeneity, and additivity, which are necessary for the theorem to hold.
Conclusion:
Thevenin's theorem is an important concept in circuit analysis, which can be used to simplify complex circuits. However, this theorem has some limitations, which should be kept in mind while applying it to circuits. The theorem can be applied to linear circuits only, whether they are passive or active. Nonlinear circuits cannot be analyzed using the theorem.
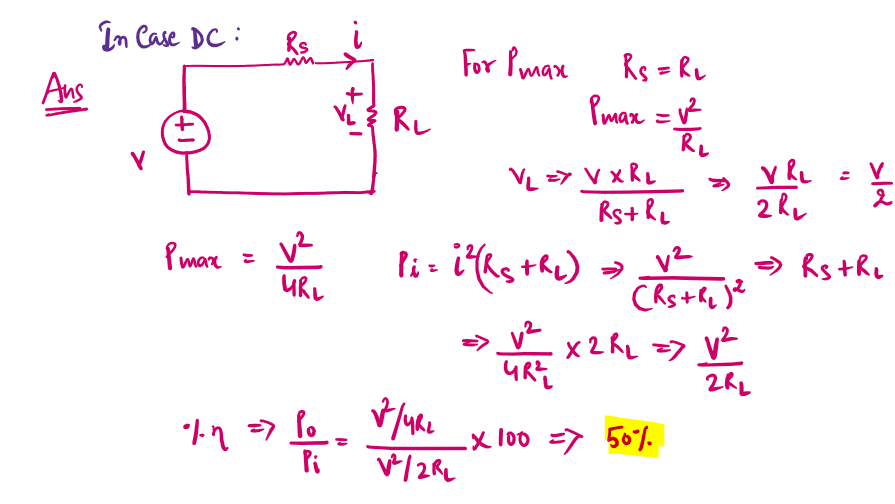
5.When a source is delivering maximum power to the load,the efficiency will be
Explain:- The maximum power transfer theorem states that, to obtain maximum external power from a source with a finite internal resistance, the resistance of the load must equal the resistance of the source as viewed from its output terminals.
The efficiency is only 50% when maximum power transfer is achieved, but approaches 100% as the load resistance approaches infinity, though the total power level tends towards zero.
7.The superposition theorem is applicable to__________
Explain:- The theorem does not apply to non-linear circuits. The requisite of linearity indicates that the superposition theorem is only applicable to determine voltage and current but not power. Power dissipation is a nonlinear function that does not algebraically add to an accurate total when only one source is considered at a time.
8.Which one of the following is applicable to any network linear or non-linear,active or passive,time varying or invarying as long as kirchhoff's laws are not violated?
Explain:- This network theorem mainly depends on Kirchhoff’s law. So, this theorem can be simply applied to the network which follows Kirchhoff’s law. This network theorem is used in circuits that have linear, nonlinear, active, passive, time-variant, or non-variant elements.
Tellegen’s Theorem Statement is, “the summation of direct power used by different elements within different branches is equivalent to zero (0) for any type of network”. This theorem works on the principle of the conservation energy principle, so used in biological and chemical applications to discover the active performance of the physical network and also used to design filters in signal processing.
The Tellegen’s theorem basic concept is being the same in a.c. or d.c circuits.
9. Which of the following theorem enables a number of voltage(or current)source to be combined directly into a single voltage(or current)source?
Explain:- Millman’s Theorem, also known as the Parallel Generator theorem, is important for calculating voltage across the load and current through the load. There are two ways to use Millman’s theorem: it can be applied to circuits containing voltage sources alone or a mixture of voltage and current sources.
Limitations of Millman’s Theorem
1.Applicable if the circuit has two or more independent sources.
2.Applicable if the circuit has no resistance between the independent source.
3.Applicable if the circuit has no dependent source between the independent source.
Applications of Millman’s Theorem
1.This theorem is very easy for calculating the voltage across a set of parallel branches which has many voltage or current sources.
2.It is easy to apply because it does not have simultaneous equations.
3.It is mostly applied for operational amplifiers connected in the series and parallel complex circuits.